Sand Casting vs. Die Casting: Which is Right for Your Project?
-
Home>
-
Blog>
-
Technology>
Sand Casting vs. Die Casting: Which is Right for Your Project?
When it comes to metal casting, selecting the right process can make or break your project. Two of the most popular methods for producing metal parts are sand casting and die casting. Each of these techniques has its own set of advantages, ideal applications, and unique characteristics. Understanding the differences between them can help you make an informed decision for your production needs.
In this blog post, we'll explore the nuances of sand casting and die casting, comparing their processes, benefits, and the types of projects they are best suited for. Whether you’re an engineer, designer, or manufacturer, this comparison will help you better understand which method is right for your needs.

Understanding Sand Casting
What is Sand Casting?
Sand casting is one of the oldest and most versatile metal casting methods. It involves creating a mold using sand, which is then filled with molten metal to form the desired shape. The process typically begins with a pattern, usually made of wood, metal, or plastic, which is used to create the mold cavity in the sand. Once the mold is prepared, the molten metal is poured into it, allowed to cool and solidify, and then the mold is removed to reveal the finished casting.
Key Features of Sand Casting
Material Flexibility: Sand casting can be used for a wide range of metals, including iron, steel, aluminum, and brass.
Cost-Effective for Small Batches: This method is often preferred for small to medium-sized production runs due to its relatively low mold creation cost.
Large and Complex Parts: Sand molds can be made to accommodate larger parts with intricate designs that may not be possible with other methods.
Customization: The process allows for a high degree of flexibility in terms of part customization.

Advantages of Sand Casting
Low Tooling Costs: Sand molds are inexpensive and easy to create, making this a great choice for prototype development or small production runs.
Design Flexibility: The method allows for complex shapes and large components that other casting methods may struggle with.
Ideal for Low-to-Medium Volume Production: While sand casting can handle larger runs, it’s especially cost-effective for smaller production needs.
Disadvantages of Sand Casting
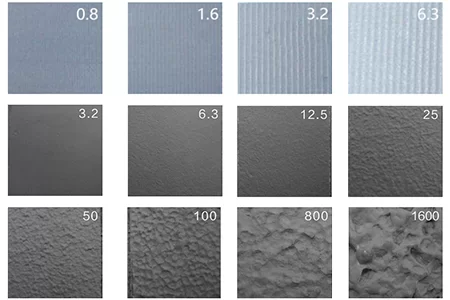
Lower Dimensional Accuracy: Compared to other casting techniques, sand casting has relatively lower dimensional accuracy. There may be some variation in the size and shape of the finished casting due to factors such as sand shrinkage and mold distortion.
Surface Finish Limitations: The surface finish of sand castings is generally not as smooth as that of other methods. Additional machining or finishing may be required to achieve the desired surface quality, which can add to the overall cost and time of production.
Understanding Die Casting
What is Die Casting?
Die casting, on the other hand, uses high pressure to inject molten metal into a steel mold, known as a die. The metal is forced into the mold at high speed, ensuring a precise shape and smooth surface finish. Die casting is commonly used for producing high-volume parts with consistent quality and intricate details.
Key Features of Die Casting
Precision: Die casting provides very tight tolerances and smooth finishes, making it suitable for parts that require high accuracy.
High-Volume Production: This method is most beneficial for mass production runs due to its ability to quickly create large quantities of identical parts.
Metal Options: Common materials used for die casting include aluminum, zinc, and magnesium alloys, which are ideal for lightweight, durable parts.

Advantages of Die Casting
High-Speed Production: Once the dies are made, die casting can produce parts very quickly, making it ideal for high-volume manufacturing.
Consistent Quality: The precision of die casting ensures that parts are identical in every run, making it an excellent choice for industries that demand uniformity.
Smooth Surface Finish: Parts produced by die casting typically require little to no post-processing due to their smooth surface quality.
Durability: Die casting produces parts with excellent mechanical properties, including strength, wear resistance, and dimensional stability.
Disadvantages of Die Casting
High Initial Tooling Costs: The cost of creating the dies for die casting can be significant, especially for complex designs. This can make it less cost-effective for prototyping or low-volume production runs.
Limited to Certain Metals: Die casting is primarily suitable for non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, zinc, and magnesium. Ferrous metals, which are more commonly used in some industries, are not typically compatible with the die casting process.
Size and Shape Constraints: There are limitations to the size and shape of parts that can be produced using die casting. Extremely large or complex geometries may require additional manufacturing steps or alternative casting methods.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Sand Casting and Die Casting
Project Requirements
Dimensional Tolerances: If your project demands extremely tight tolerances and high precision, die casting is likely the better choice. However, if some dimensional variation is acceptable, sand casting may be sufficient.
Surface Finish Requirements: For applications where a smooth surface finish is crucial, such as for visible exterior components, die casting offers superior results. Sand casting may require additional finishing processes to achieve the desired surface quality.
Production Volume: For small-scale production runs or prototypes, sand casting is often more cost-effective due to its lower initial investment. Die casting becomes more economical for large-volume production, where the benefits of high-speed production and low per-unit costs outweigh the high tooling costs.
Material Selection
Consider the properties of the metal or alloy you need to cast. If you require certain mechanical or chemical properties that are only available in ferrous metals, sand casting may be the only viable option. On the other hand, if you can work with non-ferrous metals, die casting offers excellent results.
Budget Considerations
Evaluate your budget for both tooling and production costs. If you have a limited budget and are unsure about the long-term production volume, sand casting may be a safer choice. However, if you anticipate a high production volume and can justify the upfront investment, die casting can offer significant cost savings in the long run.
In conclusion, both sand casting and die casting have their unique advantages and disadvantages. By carefully considering your project requirements, material selection, and budget, you can make an informed decision about which casting method is best suited for your needs. Whether you're producing a one-of-a-kind prototype or manufacturing parts in large quantities, understanding the differences between sand casting and die casting will help you achieve the best possible results.
So, the next time you're faced with the choice between these two popular casting methods, don't hesitate to weigh the pros and cons and select the option that aligns best with your project goals. Happy casting!
Article Navigation
Article Navigation
Industries
Foundries
-

March.18, 2025
Surface Roughness Comparison of Castings with Different Materials and Processes
READ MORE
-

March.10, 2025
Achieving Precision in Metal Casting: Key Strategies for High-Quality Casting Parts
READ MORE
-

March.03, 2025
Addressing Defects in Castings: A Comprehensive Guide
READ MORE
-

January.20, 2025
Surface Treatments for Metals After Casting
READ MORE
-

January.09, 2025
How to Select The Right Raw Materials for Casting Foundries?
READ MORE
-

December.09, 2024
Differences in Wax Materials for Precision Casting
READ MORE