
Surface Roughness Comparison of Castings with Different Materials and Processes.
-
Home>
-
Blog>
-
Technology>
Surface Roughness Comparison of Castings with Different Materials and Processes
The surface roughness of castings is one of the important indicators to measure the quality of castings, which directly affects their wear resistance, fatigue strength and subsequent processing costs. Different casting processes and materials will have a significant impact on the surface roughness of castings. Therefore, when choosing a casting process, cost, performance and processing requirements must be considered comprehensively. This article will compare the surface roughness of common casting processes and castings of different materials, and provide a comparison table to more intuitively understand their respective characteristics.
Factors Affecting Surface Roughness in Castings
Material Properties
The melting point, fluidity, and shrinkage rate of different materials influence surface quality. High-melting-point materials cool rapidly, leading to surface defects. Good fluidity ensures smooth surfaces, while high shrinkage rates may cause porosity and uneven surfaces.
Casting Process Parameters
Pouring temperature, pouring speed, mold temperature, and cooling rate affect surface roughness. High pouring temperatures may erode the mold, increasing roughness. Improper pouring speed can cause turbulence and gas entrapment. Optimized mold temperature and cooling speed promote uniform and dense surfaces.
Mold Material and Quality
Mold material properties such as grain size, hardness, and permeability affect surface roughness. Finer sand grains in sand casting produce smoother surfaces but reduce permeability. In investment casting, refractory material quality and coating thickness impact surface quality.
Release Agents and Lubricants
These substances reduce friction between molten metal and the mold, improving metal flow and easing demolding, thereby reducing surface roughness. The choice of release agents affects the final surface finish.
Mold Material and Precision
High-quality metal molds or precision-machined cavities minimize defects and enhance surface smoothness. A well-polished mold surface results in a better casting finish. Mold oxidation, deformation, or cracking at high temperatures can increase roughness, so proper mold selection and maintenance are essential.
Post-Processing Methods
Post-treatment significantly impacts surface roughness. Sandblasting removes oxidation layers, burrs, and sand residues. Polishing further reduces roughness and enhances shine. Machining (turning, milling, grinding) achieves precise surface control. Chemical treatments (acid pickling, passivation) and heat treatments (stress relief annealing) can also improve surface finish. Choosing the right post-treatment method optimizes surface quality.
Surface Roughness Comparison of Different Casting Processes
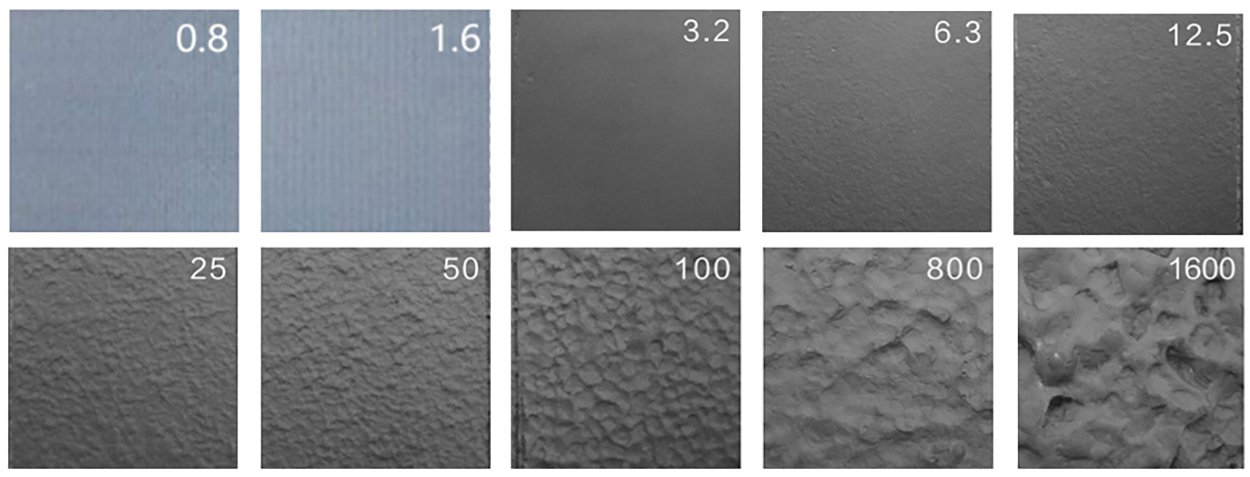
The table below summarizes the comparison of surface roughness for several common casting processes (unit: μm Ra):
Casting Process | Typical Materials | Surface Roughness Range (Ra) | Main Characteristics |
Sand Casting | Gray Iron, Ductile Iron, Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel | 6.3 - 25 | Low production cost, capable of producing large and complex parts, but with higher surface roughness |
Investment Casting (Lost Wax) | Stainless Steel, Alloy Steel, Aluminum Alloy | 1.6 - 6.3 | High surface finish, suitable for high-precision parts, but with higher cost |
Die Casting | Aluminum Alloy, Zinc Alloy, Magnesium Alloy | 0.8 - 3.2 | Excellent surface quality, suitable for mass production, but limited to low-melting-point metals |
Centrifugal Casting | Stainless Steel, Copper Alloy, Cast Iron | 1.6 - 6.3 | Suitable for cylindrical parts, good surface quality, and dense structure |
Continuous Casting | Copper Alloy, Aluminum Alloy | 0.8 - 3.2 | Suitable for the production of metal profiles, excellent surface quality |
Metal Mold Casting | Aluminum Alloy, Magnesium Alloy, Gray Iron | 3.2 - 6.3 | Better surface finish than sand casting due to the use of metal molds |
Surface Roughness Comparison of Castings with Different Casting Processes
In addition to the casting process, different metal materials will also affect the surface roughness of the casting. The following is a comparison of the surface roughness of common materials:
Materials | Common casting processes | Typical Surface Roughness Range (Ra) |
Gray Iron | Sand Casting, Metal Mold Casting | 6.3 - 25 |
Ductile Iron | Sand Casting, Metal Mold Casting | 3.2 - 12.5 |
Carbon Steel | Sand Casting, Precision Casting | 3.2 - 12.5 |
Stainless Steel | Precision Casting, Centrifugal Casting | 1.6 - 6.3 |
Alloy Steel | Die Casting, Metal Mold Casting | 0.8 - 3.2 |
Copper Alloy | Continuous Casting, Centrifugal Casting | 1.6 - 6.3 |
How to Optimize The Surface Roughness of Castings?
Select Casting Materials
Material properties affect the surface quality of castings. Materials with good fluidity, such as aluminum alloys and copper alloys, can better fill the mold cavity. Low shrinkage materials can reduce shrinkage cavities and shrinkage. Optimizing alloy composition and adding modification agents can improve the structure of castings and enhance surface quality.
Controlling Process Parameters
Reasonable adjustment of pouring temperature, speed, mold temperature and cooling rate have a significant impact on the surface roughness of castings. Appropriate pouring temperature can reduce sand scouring and metal liquid oxidation; appropriate pouring speed can avoid turbulence, bubbles and insufficient filling; control mold temperature to ensure uniform solidification; adjust cooling rate to prevent thermal cracking and shrinkage.
Select High Quality Casting Materials
The particle size, hardness and air permeability of casting materials are crucial. Fine-grained sand can improve surface finish, but it must also take into account air permeability to prevent pores. Increasing the hardness of the sand can resist metal liquid scouring. When investing in investment casting, the use of fine-grained ceramic slurry can improve the quality of the mold shell.
Use Mold Release Agents & Lubricants Skillfully
Appropriate mold release agents and lubricants can reduce the friction between castings and molds. Choose mold release agents that are stable at high temperatures and have good lubricity. Pay attention to the thickness of the coating. Too thick will affect the finish, and too thin will easily stick to the mold.
Use High Precision Molds
The quality of the mold determines the surface accuracy of the casting. Improve the mold processing accuracy to ensure smooth cavities. Use heat-resistant and wear-resistant mold materials to reduce thermal deformation, and regularly maintain and repair worn parts.
Implement post-processing technology: Post-processing can further reduce surface roughness. Sandblasting removes oxide layers and burrs, polishing improves finish, machining accurately controls flatness, and chemical treatment removes surface oxides.
Optimize Casting Technology
For parts with high surface requirements, precision casting or die casting is a good choice to better ensure surface quality.
Impact of Casting Surface Roughness on Application
Appearance Requirements
In some products with high requirements for appearance, such as decorations, medical device shells, etc., the surface roughness directly affects the beauty and texture of the product. Castings with rough surfaces may require a lot of subsequent grinding, polishing and other processing procedures, which increases costs and production cycles.
Assembly Performance
For parts that need to be assembled, surface roughness will affect the fit accuracy and sealing between parts. If the surface is too rough, it may cause uneven fit clearance, affect assembly quality, and even cause leakage and other problems.
Castings Performance
In some parts that are subjected to friction, wear or fatigue loads, surface roughness will affect the service life of the parts. Rough surfaces are prone to stress concentration and reduce the fatigue strength of parts; in friction pairs, surface roughness will also affect the friction coefficient, which in turn affects energy loss and the working efficiency of parts.
Selection Suggestions of Casting Surface Roughness on Application
Select Materials & Processes According to Application Requirements
If the appearance and dimensional accuracy of the castings are extremely high, and the shape of the parts is complex, investment casting or pressure casting may be a better choice. The material can be selected from aluminum alloys, copper alloys, etc. according to specific performance requirements. For some large, simple and cost-sensitive parts, sand casting may be more suitable, and the material can be cast iron or cast steel.
Balance Cost & Quality
The cost of different materials and processes varies greatly. When choosing, it is necessary to comprehensively consider the quality requirements and cost budget of the casting. For example, although investment casting can obtain high-quality castings, the cost is high; while sand casting has a low cost, the surface roughness is relatively large. The surface quality of sand casting can be improved to a certain extent by optimizing process parameters and improving casting materials, while controlling costs.
Consider The Difficulty of Subsequent Processing
Castings with greater surface roughness may require more subsequent processing steps, such as grinding, polishing, machining, etc. When selecting casting processes and materials, it is necessary to consider the feasibility and cost of subsequent processing. If the subsequent processing is difficult, a casting process with better surface quality should be selected as much as possible.
The surface roughness of a casting is an important indicator affected by many factors. By understanding the impact of different materials and different processes on the surface roughness of castings, we can select the appropriate casting scheme according to specific needs in actual production to obtain high-quality castings that meet performance, appearance and cost requirements. We hope that this article can provide valuable reference for readers working in the foundry industry and related fields, and provide some inspiration in the selection and optimization of casting processes.
Article Navigation
Article Navigation
Industries
Foundries
-

March.10, 2025
Achieving Precision in Metal Casting: Key Strategies for High-Quality Casting Parts
READ MORE
-

March.03, 2025
Addressing Defects in Castings: A Comprehensive Guide
READ MORE
-

February.25, 2025
How to Compare Product Quality Between Different Casting Foundries?
READ MORE
-

February.14, 2025
What Are The Metal Casting Materials Commonly Used in Foundries?
READ MORE
-

January.20, 2025
Surface Treatments for Metals After Casting
READ MORE







