Surface Treatments for Metals After Casting
-
Home>
-
Blog>
-
Technology>
Surface Treatments for Metals After Casting
Metal casting is a widely used manufacturing process that involves pouring molten metal into a mold and allowing it to solidify. However, the surface of the cast metal often requires further treatment to enhance its properties and meet specific application requirements. Surface treatments play a crucial role in improving the appearance, corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and overall performance of cast metal products. In this article, we will explore the various surface treatments commonly applied to metals after casting.
Cleaning
Cleaning is the first step in the surface treatment of cast metals. After casting, the surface of the metal may contain impurities such as sand, slag, oxides, and grease. These impurities can affect the subsequent treatment processes and the performance of the final product. There are several methods for cleaning cast metal surfaces:
Mechanical Cleaning
Mechanical cleaning methods involve physically removing impurities from the metal surface. This can be achieved through techniques such as sandblasting, grinding, and polishing. Sandblasting uses a high-velocity stream of abrasive particles to remove surface contaminants. It is effective for removing rust, scale, and paint. Grinding and polishing are used to smooth the surface and remove any roughness or imperfections.
Chemical Cleaning
Chemical cleaning involves the use of chemical solutions to dissolve or remove impurities from the metal surface. Acid pickling is a common chemical cleaning method, where an acidic solution is used to remove oxides and scale from the metal. Alkaline cleaning solutions can also be used to remove grease and other organic contaminants. Chemical cleaning is often followed by rinsing with water to remove any residual chemicals.
Heat Treatment
Heat treatment is a process that involves heating and cooling the metal to alter its microstructure and properties. After casting, heat treatment can be used to relieve internal stresses, improve the mechanical properties, and enhance the corrosion resistance of the metal. Some of the common heat treatment processes for cast metals are:
Annealing
Annealing is a heat treatment process that involves slowly heating the metal to a specific temperature and then cooling it gradually. This process helps to relieve internal stresses, improve the ductility and machinability of the metal, and reduce brittleness. Annealing is often used for castings that require further machining or forming.
Normalizing
Normalizing involves heating the metal to a higher temperature than annealing and then cooling it in air. This process helps to refine the grain structure of the metal, improve its strength and hardness, and enhance its machinability. Normalizing is commonly used for cast ferrous alloys.
Quenching and Tempering
Quenching involves rapidly cooling the heated metal in a quenching medium such as water, oil, or air. This process hardens the metal by creating a martensitic microstructure. However, quenching can also introduce internal stresses and make the metal brittle. Tempering is then carried out by reheating the quenched metal to a lower temperature and holding it for a certain period. Tempering relieves the internal stresses and improves the toughness and ductility of the metal.
Coating
Coating is a widely used surface treatment method for cast metals to provide protection, improve appearance, and enhance functionality. There are various types of coatings that can be applied to cast metal surfaces, including:
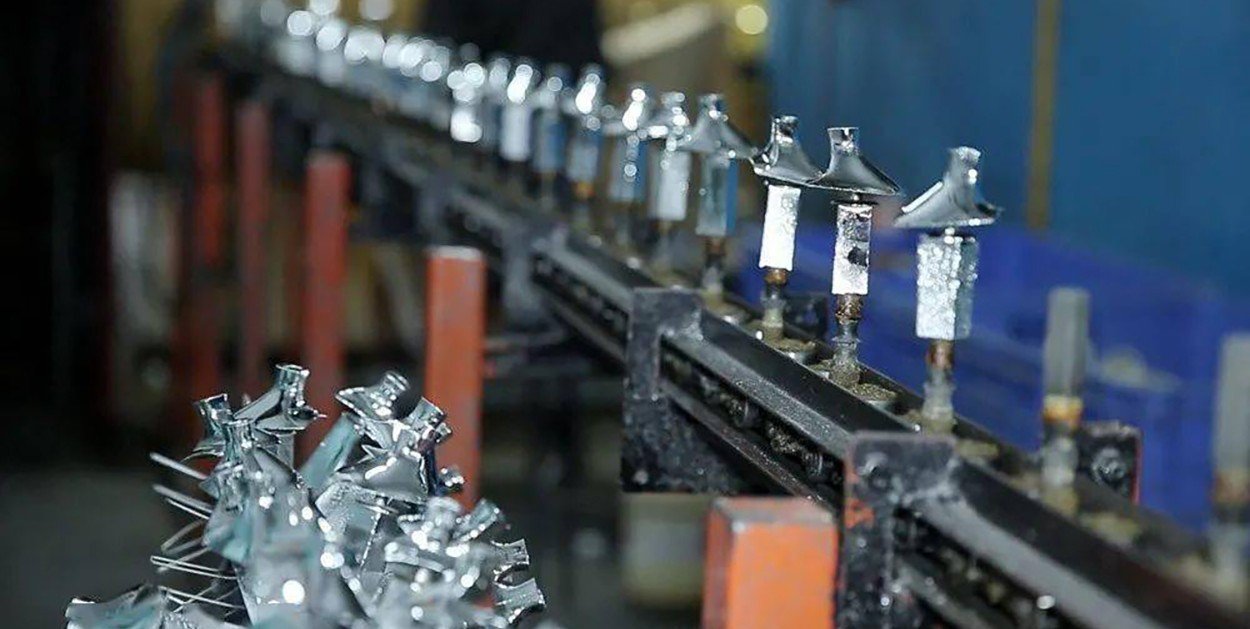

Electroplating
Electroplating is a process that involves depositing a thin layer of metal onto the surface of another metal through an electrochemical reaction. This process can improve the corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and electrical conductivity of the cast metal. Commonly plated metals include chrome, nickel, and zinc. Chrome plating provides excellent corrosion resistance and a hard, wear-resistant surface. Nickel plating offers good corrosion resistance and can be used as a base layer for other coatings. Zinc plating is often used for sacrificial protection, as zinc corrodes preferentially to the underlying metal.
Powder Coating
Powder coating is a dry finishing process in which a mixture of pigments, resins, and other additives is electrostatically charged and sprayed onto the heated metal surface. The powder particles adhere to the metal and then melt and cure during a baking process to form a uniform, durable coating. Powder coating offers a wide range of colors and finishes, excellent corrosion resistance, and good UV stability. It is commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and architecture.
Organic Coatings
Organic coatings, such as paints and lacquers, are applied to cast metal surfaces to provide protection and aesthetic appeal. These coatings consist of a binder, pigments, and solvents. Organic coatings offer good corrosion resistance, UV protection, and can be easily customized in terms of color and finish. They are often used for decorative purposes and to protect the metal from environmental factors.
Passivation
Passivation is a chemical treatment process that involves the formation of a thin, passive layer on the surface of the metal to protect it from corrosion. The passive layer is typically composed of oxides or other compounds that are less reactive than the underlying metal. Passivation is commonly used for stainless steel castings to enhance their corrosion resistance. The passivation process can improve the ability of the metal to resist pitting, crevice corrosion, and other forms of localized corrosion. It is also used in applications where the cast metal is exposed to harsh environments, such as in chemical processing plants and offshore industries.
Shot Peening
Shot peening is a cold working process in which high-velocity shot particles are directed onto the surface of the cast metal. The impact of the shot particles creates plastic deformation on the surface, which results in the formation of residual compressive stresses. These compressive stresses help to improve the fatigue resistance and wear resistance of the metal. Shot peening is often used for cast metal components that are subject to cyclic loading, such as gears, springs, and aerospace components.
Abrasive Blasting
Abrasive blasting, also known as sandblasting, is a method of cleaning and surface preparation that involves propelling abrasive particles against the surface of the cast metal at high velocity. This process not only removes impurities and roughens the surface but also improves the adhesion of subsequent coatings. Abrasive blasting can be performed using various types of abrasive media, such as sand, glass beads, aluminum oxide, and carbide grits. The choice of abrasive media depends on the material of the cast metal and the desired surface finish.
Laser Surface Treatment
Laser surface treatment is an advanced technology that uses high-energy laser beams to modify the surface properties of cast metals. This can include processes such as laser hardening, laser cladding, and laser remelting. Laser hardening involves heating the surface of the metal to a specific temperature and then rapidly cooling it to create a hardened layer. Laser cladding involves depositing a layer of metal or ceramic material onto the surface of the cast metal to improve its wear, corrosion, or thermal resistance. Laser remelting is used to refine the microstructure of the surface layer and improve its mechanical properties.
Anodizing
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that is mainly used for aluminum castings. It involves passing an electric current through an electrolyte solution in which the aluminum casting is immersed. This process forms a thick, porous oxide layer on the surface of the aluminum. The oxide layer can be dyed to provide a variety of colors and can also be sealed to improve its corrosion resistance. Anodized aluminum castings are widely used in applications such as architectural hardware, automotive components, and consumer electronics.
Phosphate Coating
Phosphate coating is a chemical conversion coating process that is commonly applied to cast iron and steel. It involves immersing the cast metal in a phosphoric acid-based solution, which reacts with the surface of the metal to form a crystalline phosphate layer. The phosphate coating acts as a primer and improves the adhesion and corrosion resistance of subsequent coatings. It is often used as a preparatory treatment for painting or powder coating.
Chromating
Chromating is a chemical treatment process that involves the deposition of a thin layer of chromium compounds onto the surface of the cast metal. Chromating coatings provide excellent corrosion resistance and can also improve the adhesion of paint and other coatings. However, due to the toxicity of chromium, there has been a growing trend towards the development of alternative, more environmentally friendly treatments.
Vapor Deposition
Vapor deposition is a process that involves the deposition of a thin film of material onto the surface of the cast metal in a vacuum environment. There are two main types of vapor deposition: physical vapor deposition (PVD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD). PVD involves the physical evaporation or sputtering of a material, which then condenses onto the surface of the metal. CVD involves the chemical reaction of gas-phase precursors to form a solid deposited on the surface. Vapor deposition can produce high-quality coatings with excellent adhesion, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance.
Electroless Plating
Electroless plating is a chemical deposition process that does not require an external electrical current. Instead, the deposition is driven by a chemical reaction between the metal ion in the plating solution and a reducing agent. Electroless plating can be used to deposit a variety of metals, such as nickel, gold, and silver, onto the surface of cast metals. This process provides a uniform and uniform coating, even on complex shapes and geometries.
Surface Modification by Ion Implantation
Ion implantation is a surface modification technique that involves bombarding the surface of the cast metal with high-energy ions. This process can alter the chemical composition and microstructure of the surface layer, leading to improved mechanical, chemical, and electrical properties. Ion implantation can be used to enhance the hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance of cast metals.
In conclusion, surface treatments are essential for improving the performance, durability, and appearance of cast metals. The choice of surface treatment method depends on various factors, including the type of metal, the application requirements, and the desired properties. Whether it is cleaning, heat treatment, coating, passivation, or other advanced surface modification techniques, each method plays a crucial role in enhancing the quality and functionality of cast metal products. By understanding and implementing the appropriate surface treatments, manufacturers can produce cast metals that meet the highest standards and satisfy the diverse needs of various industries.
At Hulk Metal, we understand the significance of these surface treatments. We are well-equipped to provide a wide range of surface treatment options tailored to our clients' specific needs. Whether it's a small - scale project requiring a decorative finish or a large - scale industrial application demanding high - performance corrosion and wear resistance, our team of experts can ensure that your castings receive the most suitable surface treatment. If you have any requirements regarding surface treatments for your castings, please do not hesitate to contact us. We are always ready to assist you in achieving the highest quality standards for your products.
Article Navigation
Article Navigation
Industries
Foundries
-

March.25, 2025
CNC Cutting vs. Laser Cutting: Which One is Right for Your Project?
READ MORE
-

March.12, 2025
Applications of Stainless Steel Castings in Medical Devices
READ MORE
-

March.03, 2025
Addressing Defects in Castings: A Comprehensive Guide
READ MORE
-

February.25, 2025
How to Compare Product Quality Between Different Casting Foundries?
READ MORE
-

February.14, 2025
What Are The Metal Casting Materials Commonly Used in Foundries?
READ MORE
-

January.20, 2025
Surface Treatments for Metals After Casting
READ MORE