CNC Milling vs. CNC Turning: Unraveling the Key Differences for Your Project
-
Home>
-
Blog>
-
Technology>
CNC Milling vs. CNC Turning: Unraveling the Key Differences for Your Project
In the dynamic world of precision machining, Computer Numerical Control (CNC) technology has revolutionized the way we create complex parts. Among the various CNC processes, CNC milling and CNC turning are two of the most commonly used methods. But how do you know which one is the best fit for your project? In this blog post, we'll break down the differences between CNC milling and CNC turning, explore their unique advantages, and help you make an informed decision.
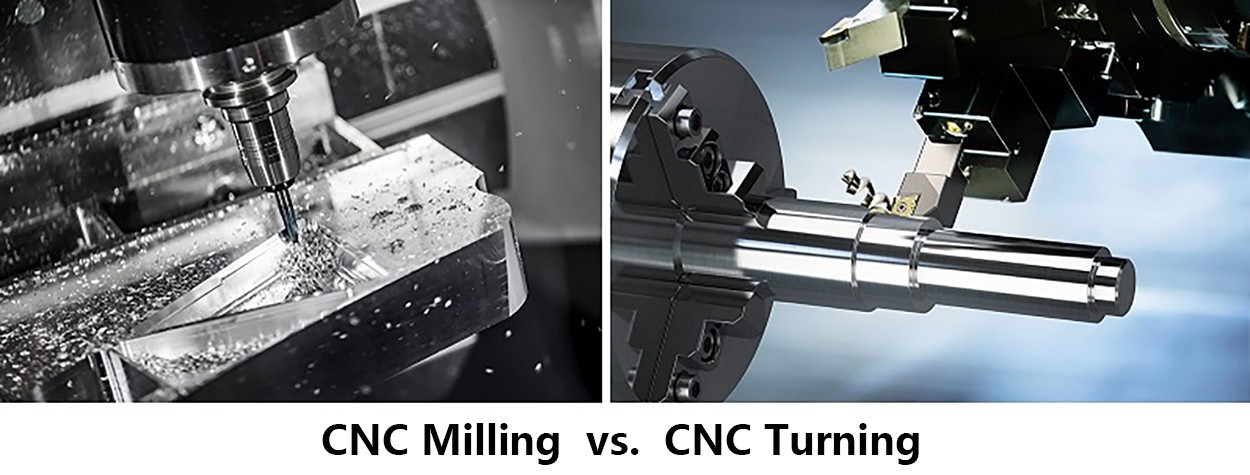
What is CNC Milling?
CNC milling is a subtractive manufacturing process that uses multi - edged cutting tools to remove material from a workpiece. The workpiece is held stationary, while the cutting tool rotates at high speeds and moves along multiple axes (usually three or more) to shape the material. Here's a step - by - step breakdown of how it works:
Workpiece Setup
The raw material, which can be a block of metal, plastic, or other suitable materials, is securely fastened to the machine's worktable.
Tool Selection
Different types of cutting tools, such as end mills, ball nose mills, and face mills, are chosen based on the shape and requirements of the final part. Each tool has a specific cutting edge geometry designed for different machining operations like slotting, contouring, and surface finishing.
Programming
A computer - aided design (CAD) model of the part is created, and then translated into a set of instructions using computer - aided manufacturing (CAM) software. These instructions tell the CNC milling machine the exact movements of the cutting tool, the speed at which it should rotate, and the depth of the cuts.
Machining
The cutting tool moves along the programmed paths, removing material from the workpiece in layers until the desired shape is achieved. The multi - axis movement of the tool allows for the creation of complex 3D shapes, including cavities, holes, and intricate surface details.
Finishing
Once the machining is complete, the part may undergo additional finishing processes like deburring, polishing, or heat treatment to meet the required specifications.
CNC milling offers great versatility, as it can produce a wide variety of parts with complex geometries. It's commonly used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and mold making, where parts with irregular shapes, deep pockets, and precise surface finishes are required.
What is CNC Turning?
CNC turning, on the other hand, is a machining process where the workpiece rotates while a single - point cutting tool removes material from its surface. The cutting tool is stationary and moves along the X and Z axes (in a two - axis turning machine) to shape the rotating workpiece. Here's how the process unfolds:
Workpiece Mounting
The raw material, typically in the form of a bar or rod, is mounted on a chuck or a collet that holds it firmly and rotates it at high speeds.
Tool Setup
Single - point cutting tools, such as turning inserts, are installed in the tool post of the lathe. These tools are designed to cut the material as the workpiece rotates.
Programming
Similar to CNC milling, a CAD model of the part is created, and CAM software is used to generate the instructions for the CNC turning machine. The program specifies the speed of the workpiece rotation, the feed rate of the cutting tool, and the depth of the cuts.
Machining
As the workpiece rotates, the cutting tool moves in a linear motion along the axis of the workpiece, gradually removing material to create the desired shape. This process is ideal for producing cylindrical parts, such as shafts, bolts, and pipes, as well as parts with tapered surfaces and threads.
Part Removal and Finishing
Once the machining is finished, the part is removed from the lathe, and any necessary finishing operations are carried out.
CNC turning is highly efficient for producing parts with rotational symmetry. It's widely used in the production of components for the automotive, medical, and consumer electronics industries, where precision - turned parts are in high demand.
Comparing CNC Milling and CNC Turning
Part Geometry
CNC milling excels at creating parts with complex 3D shapes, including parts with undercuts, angled surfaces, and irregular profiles. It can machine parts that have multiple features on different planes. In contrast, CNC turning is best suited for parts with rotational symmetry, such as cylinders, cones, and parts with concentric features. While it can create some limited non - rotational features like grooves and threads, it's not as versatile as CNC milling for complex, non - symmetrical shapes.
Production Speed
The production speed of both processes depends on various factors, but generally, CNC turning can be faster for parts with simple cylindrical shapes. Since the cutting tool only needs to move along a few axes while the workpiece rotates, it can quickly remove material and produce parts. However, for parts with complex geometries that require multiple setups and tool changes, CNC milling may take longer.
Tooling and Setup
CNC milling often requires a larger variety of cutting tools due to the diverse machining operations it can perform. Setting up a CNC milling machine for a new job may involve more complex tool changes and adjustments. CNC turning, on the other hand, typically uses fewer types of single - point cutting tools, and the setup process can be relatively simpler, especially for parts with similar geometries.
Surface Finish and Precision
Both CNC milling and CNC turning can achieve high levels of precision and good surface finishes. However, the surface finish of a part can be influenced by factors such as the cutting speed, feed rate, and the type of tool used. CNC turning can often produce a smoother surface finish on cylindrical surfaces due to the continuous rotation of the workpiece and the nature of the single - point cutting tool. CNC milling, with its ability to use different types of tools for finishing operations, can also achieve excellent surface quality, especially for parts with complex shapes.
Cost
The cost of CNC machining depends on factors like production volume, part complexity, and the time required for machining. For low - volume production of simple cylindrical parts, CNC turning may be more cost - effective due to its relatively simple setup and faster production speed. For complex parts with irregular shapes, CNC milling may be more expensive initially due to the need for more tooling and longer machining times, but it can be a better choice for parts that require a high degree of customization.
Which One Should You Choose for Your Project?
The choice between CNC milling and CNC turning depends on several factors, including the part geometry, material requirements, production volume, and budget. Here are some guidelines to help you make the right decision:
Choose CNC Milling If:
You need to produce parts with complex geometries and detailed features.
The part geometry is not primarily cylindrical or rotational.
You are working on a low to medium production volume.
Precision and tight tolerances are critical for your application.
Choose CNC Turning If:
Your parts are cylindrical or rotational in shape.
You require high-speed and efficient production for large quantities.
The part geometry is relatively simple and does not require complex features.
Cost-effectiveness is a primary concern, especially for large-scale production.
Both CNC milling and CNC turning have their unique advantages and limitations. Understanding the differences between these two machining processes is essential for choosing the right method for your project. Of course, deciding between CNC milling and CNC turning ultimately comes down to the specific requirements of your project.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving field of precision machining, understanding the nuances of CNC milling and CNC turning can give you a competitive edge. By carefully evaluating your part's design, production volume, and budget, you can select the right CNC process to bring your ideas to life with the highest quality and efficiency.
If you're still unsure which process is right for your needs, don't hesitate to reach out to our team of experts. At Hulk Metal, we have our own CNC machining workshops and can provide you with both CNC milling and CNC turning services and the guidance and support you need to bring your ideas to life. Contact us today to learn more about our capabilities and how we can help you achieve your manufacturing goals.
Article Navigation
Article Navigation
Industries
Foundries
-

March.26, 2025
Sand Casting vs. Die Casting: Which is Right for Your Project?
READ MORE
-

March.25, 2025
CNC Cutting vs. Laser Cutting: Which One is Right for Your Project?
READ MORE
-

March.10, 2025
Achieving Precision in Metal Casting: Key Strategies for High-Quality Casting Parts
READ MORE
-

March.06, 2025
CNC Machining vs. Metal Casting: Unraveling the Differences for Optimal Manufacturing
READ MORE
-

March.03, 2025
Addressing Defects in Castings: A Comprehensive Guide
READ MORE