Everything You Need to Know About Die Casting!
-
Home>
-
Blog>
-
Technology>
Everything You Need to Know About Die Casting!
In the world of metal manufacturing, die casting stands out as a popular and efficient process. It's a method that has been widely used across various industries for producing high - quality metal parts with precision. In this article, we'll delve into the details of die casting, from its basic concept to its applications, limitations, and how to choose the right die casting service provider.
What is Die Casting?
Die casting is a metal manufacturing process that involves injecting molten or semi-liquid metal into a pre-designed mold cavity under high pressure, allowing it to solidify and form a part with the desired shape. This process enables the production of parts with high dimensional accuracy, smooth surface finish, and excellent mechanical properties.
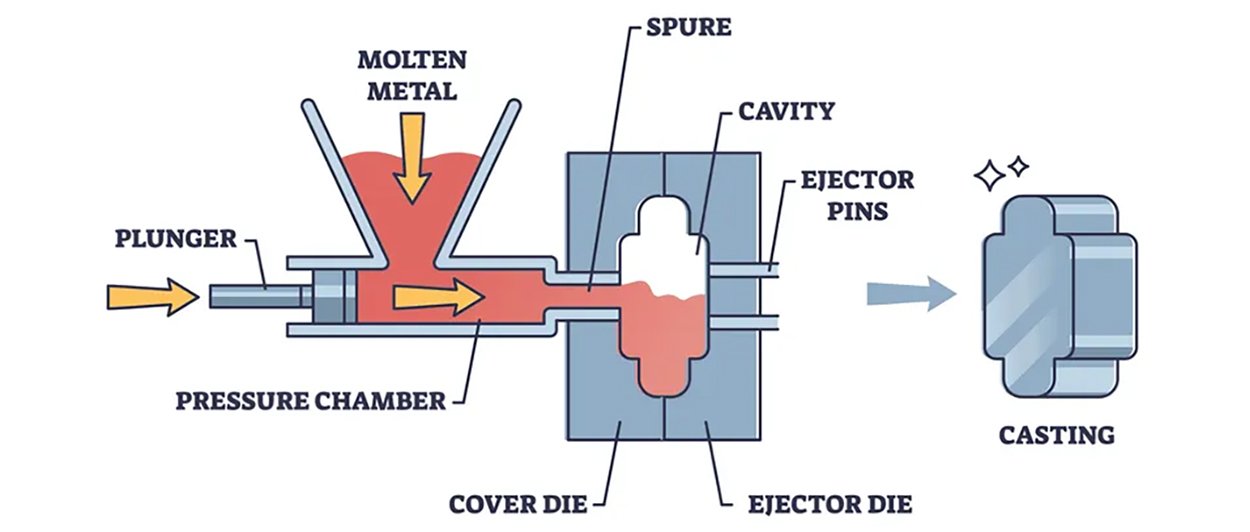
The Die Casting Process
Mold Preparation
Die casting molds come in different sizes and designs to suit various production needs. There are several common types of dies:
Single-Cavity Die: The simplest type, with one cavity that produces one part per cycle.
Multi-Cavity Die: A more complex design with identical cavities, capable of producing multiple identical parts per cycle, ideal for mass production.
Combination Die: Contains cavities of different designs, offering greater flexibility to produce various types of parts per cycle.
Unit Die: Specialized for manufacturing complex geometric parts without sacrificing precision.
After manufacturing, the mold is thoroughly cleaned to remove any contaminants that could affect the quality of the parts. It is also preheated to prevent thermal defects such as cracks that may occur due to a significant temperature difference between the mold and the molten metal.
Metal Melting
The metal to be cast is melted in a furnace. The melting process must be carefully controlled to ensure the proper composition and temperature of the molten metal. Different metals have different melting points and requirements, so appropriate melting techniques and equipment are used accordingly.
Die Casting Molding
The molten metal is injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. This process can be carried out using either a hot-chamber or cold-chamber die casting machine, depending on the type of metal being cast.
Cooling and Solidification
Once the molten metal is injected into the mold, it is allowed to cool and solidify to form the final part. The cooling process should occur while the mold is still clamped. In some cases, cooling may be carried out under pressure to prevent shrinkage and other defects.
Mold Opening and Part Ejection
After the part has fully solidified, the mold is opened, and the ejection mechanism is activated to push the solidified part out of the mold. Lubrication and the use of draft angles in the mold design facilitate easier ejection of the part.
Deburring and Finishing
The die-cast part undergoes deburring and finishing processes to remove flash and other imperfections that may leave excess material on the part. Post-processing techniques like grinding can also be used to achieve tighter tolerances. Additionally, various metal surface treatments can be applied to improve the mechanical properties, functionality, and appearance of the die-cast part.
Materials for Metal Die Casting
Die casting offers a wide range of material options, with non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, magnesium, and zinc alloys being commonly used. These metals have unique properties that make them suitable for specific applications. Here is a comparison of some common die casting alloys:
Alloy | Common Subtypes | Main Components | Melting Point (°C) | Main Characteristics and Applications |
Aluminum Alloy | A380, A360, A390, A413, ADC12 | Aluminum (Al), Copper (Cu), Silicon (Si), Magnesium (Mg) | 577 - 660 | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, high strength, and good machinability. Widely used and cost-effective for applications in automotive, aerospace, electronics, and consumer goods. |
Magnesium Alloy | AZ91D, AM60B, AS41B | Magnesium (Mg), Aluminum (Al), Zinc (Zn) | 632 - 650 | Extremely lightweight and excellent casting properties. Ideal for weight-sensitive applications in aerospace, automotive, and electronics (e.g., handheld devices). |
Zinc Alloy | #2, #3, #5, #7, ZA8, ZA27 | Zinc (Zn), Aluminum (Al), Copper (Cu), Magnesium (Mg) | 381 - 419 | Excellent casting properties, low melting point, suitable for complex designs. Cost-effective, used in electronics, hardware, toys, and automotive components. |
Applications of Die Casting Parts
Die casting is suitable for various industries that utilize non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, zinc, and magnesium. Here are some examples:
Aerospace
Die casting is used to manufacture components like engine housings and brackets in the aerospace industry, which rely on the use of materials like aluminum alloy (e.g., ADC12, A380) and magnesium alloy (e.g., AZ91D).
Automotive
The automotive industry utilizes die casting to produce engine parts (e.g., cylinder heads, gearbox housings, engine blocks) and body parts (e.g., wheel rims, door handles).
Electronics
It is suitable for manufacturing electronic components such as connectors, heat sinks, and housings.
Consumer Goods
Items like kitchen utensils, power tools, and other hardware are often manufactured using die casting with aluminum, zinc, and tin alloys.
Limitations of Metal Die Casting
While die casting offers numerous advantages, it also has some limitations:
Only for Non-Ferrous Metals
Die casting is mainly suitable for non-ferrous metals with moderate melting points. Metals like steel and iron, which have high melting points, require special equipment for casting.
High Mold Costs
The manufacturing of die casting molds is expensive due to the need for precision machining and the use of high-quality materials.
Sensitivity to Defects
Die-cast parts may be prone to defects such as porosity, shrinkage, and surface imperfections, depending on the casting process and conditions.
Not Suitable for Small Projects
The initial investment cost for die casting is relatively high, including setup costs and mold manufacturing. Therefore, it is more suitable for large-scale production where the unit cost can be reduced.
Comparison of Die Casting with Other Manufacturing Processes
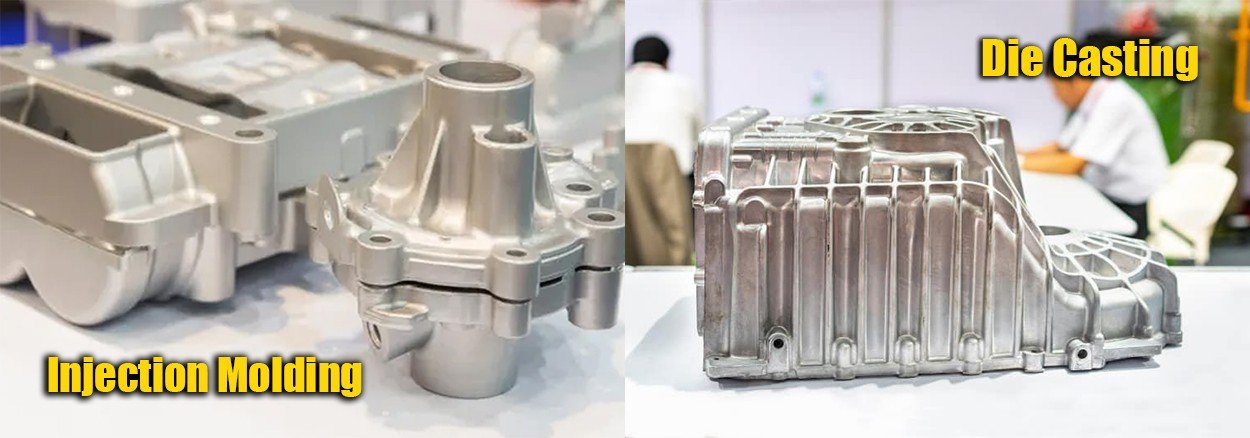
Differences between Die Casting and Injection Molding
Aspect | Die Casting | Injection Molding |
Process | Injecting molten metal into a steel mold under pressure | Injecting molten plastic into a steel or aluminum mold under pressure |
Material | Non-ferrous metal alloys (e.g., aluminum, zinc, magnesium) | Thermoplastic or thermosetting plastics |
Mold Material | Steel | Steel or aluminum |
Cooling Time | Longer | Shorter |
Production Speed | Relatively slower | Faster |
Processing Cost | Higher (due to steel molds) | Lower (due to aluminum or plastic molds) |
Part Cost | Higher (due to longer production time) | Lower (due to faster production time) |

Differences between Die Casting and Forging
Aspect | Die Casting | Forging |
Process | Injecting molten metal into a pre-designed mold under pressure | Shaping metal by applying compressive forces |
Material | Suitable for non-ferrous metals (e.g., aluminum, zinc, magnesium) | Suitable for both ferrous and non-ferrous metals (e.g., steel, aluminum) |
Molding Material | Requires molds | Does not require molds, but molds are used in some cases |
Production Speed | Faster | Slower |
Tolerance Control | High precision due to precision mold manufacturing | Moderate tolerances |
Final Part Properties | Mechanical properties depend on the casting material | Forging process improves mechanical properties |
Choosing The Right Die Casting Service Provider
Although die casting is a relatively simple metal manufacturing process in principle, it requires rich knowledge and experience to truly achieve high-precision and high-quality production. The use of advanced die casting technology is the key to ensuring product precision and quality. Therefore, outsourcing die casting business to a professional and suitable service provider is often a wiser choice.
Take Hulk Metal as an example. We have an experienced team of engineers and have accumulated many years of practical experience in the field of die casting services. We can provide you with professional and accurate die casting process recommendations based on your project needs. As an ISO 9001:2015 certified company, we are equipped with state-of-the-art production facilities and are committed to producing high-quality metal parts for our customers. If you have any related needs, please contact us. Just send us your drawings or samples, and you will get a reasonable quote and customized solutions within 24 hours.
Conclusion
Die casting is a powerful and efficient manufacturing process that produces high-quality metal parts with extreme precision. By understanding its advantages, limitations, and applications, companies can make an informed decision when choosing the right manufacturing method. If you are looking for a reliable die casting service provider, Hulk Metal is ready to provide you with tailor-made professional solutions. Please contact us.
Article Navigation
Article Navigation
Industries
Foundries
-

March.25, 2025
CNC Cutting vs. Laser Cutting: Which One is Right for Your Project?
READ MORE
-

March.10, 2025
Achieving Precision in Metal Casting: Key Strategies for High-Quality Casting Parts
READ MORE
-

March.03, 2025
Addressing Defects in Castings: A Comprehensive Guide
READ MORE
-

January.20, 2025
Surface Treatments for Metals After Casting
READ MORE
-

January.09, 2025
How to Select The Right Raw Materials for Casting Foundries?
READ MORE
-

December.09, 2024
Differences in Wax Materials for Precision Casting
READ MORE